Unveiling the Charms of Spreewald: Nature and Culture
poellauer-news >> Travel>> Unveiling the Charms of Spreewald: Nature and Culture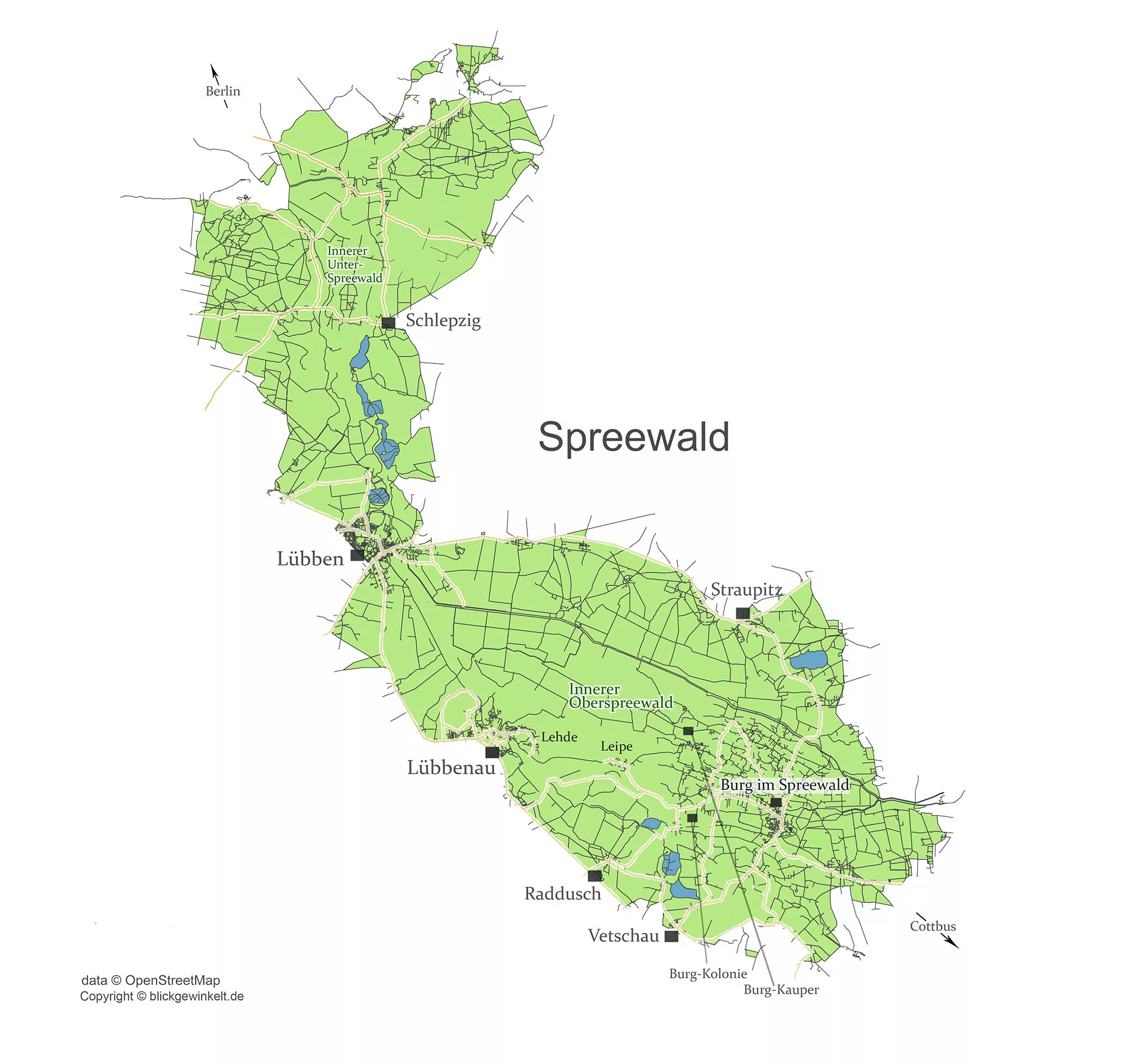
Unveiling the Charms of Spreewald: Nature and Culture
Introduction to Spreewald
Spreewald, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve located in Germany, is renowned for its breathtaking landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and traditional commerce. This picturesque region in the state of Brandenburg is characterized by a unique network of waterways, consisting of over 200 small channels and 1500 kilometers of navigable waterways. Spreewald’s ecological significance and its cultural history make it an essential topic of discussion for both nature enthusiasts and cultural tourists.
Natural Significance of Spreewald
The distinct wetland ecosystem of Spreewald is home to various plant and animal species, some of which are rare. The area boasts a vibrant biodiversity, including numerous species of birds, amphibians, and aquatic life. Efforts have been made to preserve this unique environment, leading to sustainable tourism practices that benefit both the ecosystem and local communities while allowing visitors to enjoy canoeing, cycling, and hiking. The annual floods rejuvenate the soil, making Spreewald an ideal setting for agriculture, particularly for its famed gherkins.
Cultural Richness and Traditions
Spreewald is not only known for its natural beauty but also for its rich cultural traditions, including the famous Spreewald gherkins, which have become synonymous with the region. The pickling process used for these gherkins has been passed down through generations, and locals take great pride in their traditional methods. The Spreewälder Gurkentage, or Spreewald Gherkin Days, celebrated every summer, highlights the region’s culinary heritage and attracts food lovers from across the globe.
Additionally, the local Sorbian culture, a Slavic minority, adds to the region’s uniqueness. Visitors can experience traditional Sorbian festivals, music, and costumes, solidifying Spreewald’s identity as a melting pot of cultures.
Economic Impact of Tourism
Tourism plays a vital role in Spreewald’s economy, with millions of visitors flocking to the area each year. The picturesque landscape and cultural heritage draw tourists who seek both relaxation and adventure. Local businesses, from hospitality to agriculture, benefit significantly from the influx of tourists, driving economic growth in the region.
Conclusion
Spreewald is more than just a beautiful landscape; it is a vital ecological and cultural hub reflecting Germany’s diverse heritage. As sustainable tourism continues to grow, the region’s unique natural and cultural elements will remain crucial in attracting visitors and preserving its biodiversity for future generations. The ongoing commitment to protecting Spreewald’s environment while promoting cultural traditions will ensure that this timeless region remains an important destination for years to come.